Available in strip
Clad Metals are pushing the frontiers of manufacturing and design through innovative material solutions. By combining metals, it is possible to create a material that capitalises on the superior properties that do not exist in a single metal. These properties include strength, corrosion resistance, thermal and electric conductivity, weight, surface finish, cost, even material availability.
Popular Configurations
Stainless Steel Clad Aluminium


Typical Materials include: Aluminium Alloy: 1100, Alloy 502 Stainless Steel: 301, 304, 430
Copper Clad Stainless Steel
Typical Materials include: Copper: C1100 (C101), C10200, C12200 (C106) Stainless Steel: 301, 304, 430
Copper Clad Aluminium



Typical Materials include: Copper: C1100 (C101), C10200 Aluminium Alloy: 1100, Alloy 502
Nickel Clad

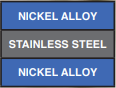
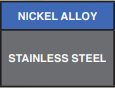
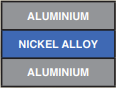

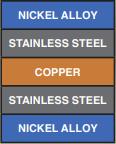
Typical Materials include: Nickel Alloy: 201 Copper: C1100 (C101), C10200, Aluminium Alloy: 1100, Alloy 502, Stainless Steel: 301, 304, 430
What are the benefits of using Clad Metals?
Materials can be combined to create an ideal combination of strength, corrosion resistance, thermal and electric conductivity, weight, surface finish with almost any combination of properties are possible. This can offer lower cost material options and overcome material availability concerns.
Clad metal is created by laminating two or more different, but compatible, metal alloys together through a process known as “clad lamination” or bonding. This joining process is also known as cladding. is typically done by applying heat and pressure to the metals. By combining metals, it is possible to create a material that capitalises on the superior properties that do not exist in a single metal. These properties can include the ideal combination of strength, corrosion resistance, thermal and electric conductivity, weight, surface finish, cost, and even material availability. As a result, designers, engineers and manufacturers are given the freedom and flexibility to create new solutions with targeted properties for even the most unique design challenges. By using Clad materials over more traditional alloys, manufacturers can achieve faster production times, a reduction in costs and a more innovative approach to designing components.
Clad metals are characterised by their strength and versatility, and as they consist of a number of layers, there are infinite combinations possible.
Modern manufacturing increasingly requires an innovative approach to overcoming a variety of challenges, including material costs, manufacturing lead times, changes to end uses and environments, and even material availability. With complex and competing demands, a single material cannot always provide a single solution. As a result, composite materials are a rapidly growing industry, and manufacturers are turning to these custom alternatives for applications across multiple sectors.
The array of clad metal configurations provides manufacturers with the opportunity to tailor-make the optimum material for their needs. Clad aluminium is one of the most popular material choices owing to the availability and low cost of aluminium alongside its many beneficial mechanical properties.
While we may be familiar with Clad material use in construction applications, we actually encounter Clad Materials on a daily basis, from decorative items such as jewellery to functional uses such as in our currency and countless electronic devices. Clad Metal is both an economical and practical choice for a wide variety of applications and sectors, including Aerospace, Petrochemical, Oil and Gas, Construction, Telecommunications, Domestic Appliances, Electronics, Medical and Defence, use Clad Metals for this reason. In addition to being widely used in electrical component production, the aerospace industry also extensively use Clad Metals in the manufacture of jet engine components, shielding and other components.
Sourcing the right material for a wide range of products is our speciality. Through exclusive supplier partnerships, we can offer you a bespoke clad metal solution to meet your needs. If you would like help in finding the right product for you, get in touch with our Sales Team today.
| CLAD METAL RANGE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base Material (Substrate) | Inlay Material | Substrate Thickness | Substrate Width | Inlay Depth |
| Aluminium Alloys, Copper Alloys, Bronze, Nickel Alloys, Stainless Steel Alloys | Aluminium Alloys, Copper Alloys, Stainless Steel Alloys, Nickel Alloys | 0.05 mm - 2.54 mm (0.002” - 0.100”) | upto 7.00” | 2-40% of the total thickness from 2.54 mm (0.100”) |
| Other material combinations are available upon request, including Titanium and Magnesium. Please contact our Sales Team with your requirements. | ||||
| CLAD ALUMINIUM RANGE | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base Material | Cladding Material | Cladding Thickness | Thickness (mm) | Width (mm) | Temper |
| 3003 | 4004, 4045, 4343, 7072 (on one or both sides) | 2.5% ± 1% | 0.30 - 3.00 | 900 - 1350 | F, O, H111, H14, H16, H18, H22, H24, H26, H28 |
| 3% ± 1% | |||||
| 4% ± 1% | |||||
| 5% ± 1% | |||||
| 6.5% ± 1.5% | |||||
| 7.5% ± 1.5% | |||||
| 10% ± 2% | |||||
| 12% ± 2% | 3.10 - 6.00 | 900 - 1350 | F, O, H111, H12, H22, H24 | ||
| 13% ± 2% | |||||
| 14% ± 2.5% | |||||
| 14% ± 3% | |||||
| 15% ± 2.5% | |||||
| 15% ± 3% | |||||
| Other specifications available upon request. | |||||
All data is provided for informational purposes only. In no event will the Knight Group and its subsidiaries, be liable for in respect of any action taken by any third party arising from using the information taken from our online or printed sources. Chemical and Mechanical Properties should not be construed as maximum or minimum values for specifications, nor should information be used to assess suitability for a particular use or application. The information and data provided is deemed to be accurate to the best of our knowledge and may be revised anytime without notice and assume no duty to update